The ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid Transmission, particularly in its advanced versions, is a highly regarded automatic gearbox employed in numerous high-performance vehicles. Its smooth shifting capabilities and operational efficiency are largely due to an intricate network of solenoids embedded within the valve body. These solenoids act as electronically controlled valves that manage fluid pressure to engage specific clutches and facilitate gear changes. For technicians dealing with this system, understanding the ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid diagram is essential for effective diagnostics and repair procedures.
In-Depth Understanding of the ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid System
This guide provides detailed insights into the ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid system, equipping professionals with the information needed to:
- Recognize the various solenoids and their specific roles.
- Interpret the hydraulic pressure flow within the valve body system.
- Troubleshoot and resolve issues related to solenoid malfunctions.
By the conclusion of this guide, you will have a comprehensive understanding of the ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid transmission, making complex repairs and diagnostics far more approachable.
Identifying the Key Components in the ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid System
The initial step to mastering the ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid system is identifying the distinct solenoids present within this advanced transmission. Below is an overview of the core solenoids you’ll commonly encounter:
- Pressure Control Solenoids (EDS): These solenoids regulate the overall line pressure within the transmission. There are usually several EDS solenoids, each numbered (e.g., EDS 1, EDS 2) and responsible for managing pressure in specific areas.
- Shift Solenoids (SL): These solenoids control the application of particular clutches by directing hydraulic pressure. For instance, the SL1 solenoid manages the A/C clutch, while SL2 oversees the B clutch.
- Torque Converter Lockup Solenoid (TCC): This solenoid controls the engagement of the torque converter clutch, which is vital for optimizing fuel efficiency during cruising.
- Manual Valve (MV): Sometimes referred to as the EPC (Electronic Pressure Control) solenoid, this solenoid modulates the overall pressure directed to the shift solenoids, thus influencing shifting behavior.
It’s important to note that the precise arrangement and naming of solenoids may differ slightly depending on the vehicle model. Always consult the specific ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid Diagram found in your vehicle’s service manual for accurate information.
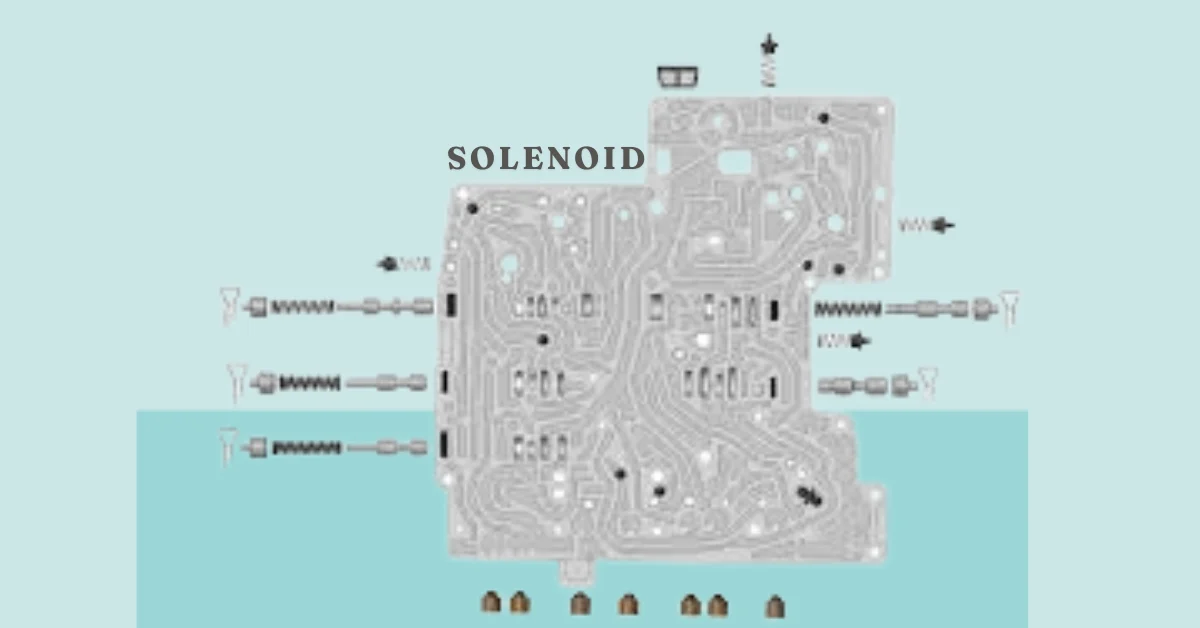
Interpreting the ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid Diagram
A ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid diagram acts as a schematic of the valve body, showing the locations and functions of each solenoid. Here’s how to decipher the key components of such a diagram:
- Solenoid Symbols: Each solenoid is represented by a specific symbol, typically a rectangle with internal markings denoting its function (pressure control, shifting, etc.).
- Hydraulic Fluid Pathways: The lines on the diagram show the routes that hydraulic fluid follows through the valve body, connecting solenoids, control valves, and clutch cylinders.
- Directional Arrows: Arrows on the pathways indicate the direction of fluid flow whenever a particular solenoid is engaged.
- Pressure Indicators: Some diagrams incorporate color coding or specific labels to indicate varying pressure levels throughout the system.
Understanding these diagrammatic elements helps you trace hydraulic pressure as it’s adjusted by the solenoids. For instance, by tracking a specific shift solenoid’s activation and the corresponding hydraulic flow, you can visualize how a clutch engages and a gear shift occurs.
Common Solenoid-Related Issues in ZF 6HP Generation 2 Transmissions
Solenoids are electronic components subject to wear over time, and issues with them can disrupt transmission performance. Below are some frequent problems associated with failing solenoids:
- Shifting Malfunctions: Erratic gear shifts, delays in engagement, or slipping between gears are indicative of a faulty shift solenoid.
- Line Pressure Problems: A defective pressure control solenoid can lead to either too much or too little line pressure, causing harsh gear changes or power transfer issues.
- Torque Converter Shudder: A malfunctioning TCC solenoid can cause vibrations during the engagement of the torque converter lockup, particularly noticeable at cruising speeds.
Procedure for Replacing and Repairing ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoids
While basic troubleshooting is possible, replacing or repairing solenoids within the ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid transmission valve body requires expertise. Below is an outline of the general process:
- Disassembling the Valve Body: The transmission needs to be removed from the vehicle, and the valve body carefully taken apart. This involves removing a variety of valves, springs, and seals, which must be handled with precision.
- Replacing Faulty Solenoids: Once the defective solenoids are identified, they are replaced with OEM or high-quality aftermarket parts. It’s essential to clean and lubricate surrounding components to ensure smooth reinstallation.
- Reassembling the Valve Body: The valve body is reassembled meticulously, ensuring each part is correctly placed and torqued according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Particular attention should be paid to valve clearances and the alignment of all components.
- Reinstalling the Transmission and Calibration: After the valve body is reinstalled, the entire transmission is remounted to the vehicle. In some cases, the Transmission Control Module (TCM) may need reprogramming or recalibration to work seamlessly with the new solenoids.
The Importance of Quality Components and Precise Procedures
Using high-quality replacement solenoids is essential for long-term transmission performance. Inferior components can cause premature failures, leading to more costly repairs. Moreover, strict adherence to the ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid service manual during disassembly and reassembly ensures proper functionality, avoiding potential issues like leaks or operational malfunctions.
Additional Resources for ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid Information
For those seeking more in-depth information about the ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid Diagram and valve body operation, consider utilizing these resources:
- ZF Technical Documentation: ZF offers comprehensive technical documentation and service manuals for their transmission systems. Some materials may require a subscription, but they provide crucial details for professionals.
- Transmission Parts Suppliers: Reliable suppliers of transmission parts often offer detailed catalogs with specifics on solenoids compatible with the ZF 6HP Generation 2. These resources frequently include technical data and solenoid replacement guidelines.
- Online Repair Communities: Experienced technicians and transmission builders often participate in online forums, sharing invaluable advice and troubleshooting tips for working on ZF 6HP Generation 2 transmissions.
Conclusion: Mastering the ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid System
Gaining a thorough understanding of the ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid system enables you to grasp the complexities of this advanced transmission. Equipped with this knowledge, you’ll be better prepared to diagnose solenoid-related problems and carry out essential troubleshooting. However, for intricate repairs involving valve body disassembly, always consult a certified transmission expert.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Here are 10 frequently asked questions about the ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid system:
- What is the ZF 6HP Generation 2 transmission?
The ZF 6HP Generation 2 transmission is an automatic gearbox found in high-performance vehicles, recognized for its smooth shifting and efficiency. - What role do solenoids play in this transmission?
Solenoids function as electronically controlled valves that regulate hydraulic fluid pressure to engage clutches and enable gear changes. - How many solenoids are in a typical ZF 6HP Generation 2 transmission?
A typical ZF 6HP Generation 2 transmission includes several solenoids, such as pressure control solenoids (EDS), shift solenoids (SL), torque converter lockup solenoids (TCC), and manual valves (MV). - What are the symptoms of a failing shift solenoid?
Symptoms of a failing shift solenoid include erratic gear changes, delayed engagement, and gear slippage. - How can solenoid-related issues be diagnosed?
Solenoid problems can be diagnosed by checking for transmission error codes, monitoring shifting behavior, and performing hydraulic pressure tests. - Is it safe to replace solenoids without professional help?
While basic troubleshooting can be done by experienced technicians, solenoid replacement requires disassembly of the transmission and should be handled by professionals. - What tools are needed for solenoid replacement?
Necessary tools include a socket set, torque wrench, screwdrivers, and the vehicle’s service manual for detailed disassembly and reassembly procedures. - How frequently should solenoids be replaced?
Solenoids don’t have a fixed replacement interval, but they should be checked regularly if shifting issues or fluid leaks occur. - Can low-quality solenoids harm my transmission?
Yes, using low-quality solenoids can lead to premature failure and additional transmission problems, compromising performance. - Where can I find more information on the ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid system?
Detailed information can be found in ZF technical documentation, from transmission parts suppliers, or through online repair forums focused on transmission maintenance.

